10 Technologies That Will Disrupt Financial Services In The Next 5 Years
SUBSCRIBE NOW GET THE FINANCIAL BRAND NEWSLETTER FOR FREE – SIGN UP NOW
The scope and speed of evolution in regulation, customer behavior and technology – coupled with the emergence of new competitors – mean that the future of banking will not be a continuation of the past. New technologies will transform banking as we know it, providing both opportunities and challenges for financial institutions.
 A decade after the financial crisis, the near-collapse of the economic system is fading from memory. But, while the banking industry has largely recovered from a financial perspective, there are storm clouds on the horizon. While capitalization has improved significantly, revenue growth has become more challenging with the strategy of cutting costs having run its course. At the same time, banks and credit unions are playing catch up from a technology perspective at a time when consumer expectations are increasing exponentially.
A decade after the financial crisis, the near-collapse of the economic system is fading from memory. But, while the banking industry has largely recovered from a financial perspective, there are storm clouds on the horizon. While capitalization has improved significantly, revenue growth has become more challenging with the strategy of cutting costs having run its course. At the same time, banks and credit unions are playing catch up from a technology perspective at a time when consumer expectations are increasing exponentially.
Making the banking business even more difficult, smaller fintech and large techfin companies are developing solutions that use insight and digital technology to improve the customer experience across product lines. These new competitors threaten legacy financial institutions of all sizes. According to various consultancies, new players could capture up to a third of incumbent banks’ revenues in the next 2-3 years. Failing to respond could lead to the demise of less agile organizations.
 The good news is that many of the new technologies that are threatening the banking industry also present significant opportunities. In fact, those organizations that can leverage big data, advanced analytics and new technologies to improve the customer experience can build trust, loyalty and revenues that are the keys to success in the future. According to Dan Cohen, Senior Vice President, Global Financial Services and Insurance at Atos, “Banks are at a crossroads. Continuous finTech innovation and new technologies such as blockchain are disrupting the market. While it creates threats, it also opens multiple opportunities for financial services to reinvent themselves and thrive.”
The good news is that many of the new technologies that are threatening the banking industry also present significant opportunities. In fact, those organizations that can leverage big data, advanced analytics and new technologies to improve the customer experience can build trust, loyalty and revenues that are the keys to success in the future. According to Dan Cohen, Senior Vice President, Global Financial Services and Insurance at Atos, “Banks are at a crossroads. Continuous finTech innovation and new technologies such as blockchain are disrupting the market. While it creates threats, it also opens multiple opportunities for financial services to reinvent themselves and thrive.”
Major Financial Trends Impacting Banking
According to research from Atos, the four most transformational challenges and opportunities for the future of banking through the next 5 years include:
- Response to customer needs. Ranked as the most important trend in each of the last 4 years in research done by the Digital Banking Report, financial institutions need to shift from physical interactions to digital engagement. For banks and credit unions that digitize customer journeys, there can be a significant benefit in revenues, cost reductions and customer satisfaction.
- Optimization of costs. Because of the efficiencies of digital-only competition, banks and credit unions will need to consider divesting from non-core operations and leveraging intelligent automation. In addition, organizations will need to reinvent back office processes and replace aging infrastructure.
- Creation of new revenue streams. Open banking and the use of APIs will open new opportunities for both cost reduction and revenue growth. As the banking ecosystem expands beyond traditional banking services, new products will be developed and segments served that will provide differentiated offerings and monetization opportunities.
- Development of security and compliance systems. With customer data becoming a ‘product’ for many financial institutions, the need for enhanced security and advanced insights (AI) will become a differentiator from both a compliance and customer trust perspective. This can lead to reduced costs and potential business growth.
Expanding Digitalization and Innovation
 Siloed systems that have traditionally been used for transaction, savings, investment and loan accounts are not well suited for the level of agility and scalability required for the digital age. As discussed in depth in the 108-page Innovation in Retail Banking2018 report, banks and credit unions have responded with an increasing array of digitalization and innovation initiatives, using cloud technologies, advanced analytics and new distribution alternatives to respond to consumer expectations.
Siloed systems that have traditionally been used for transaction, savings, investment and loan accounts are not well suited for the level of agility and scalability required for the digital age. As discussed in depth in the 108-page Innovation in Retail Banking2018 report, banks and credit unions have responded with an increasing array of digitalization and innovation initiatives, using cloud technologies, advanced analytics and new distribution alternatives to respond to consumer expectations.
All of these initiatives have three things in common, according to the Atos research.
- Customer-centric perspective
- Real-time intelligent data integration
- Open platform foundation
Some of this transformation will require the development of partnerships or expanded collaboration with outside organizations. Others will require modernization of outdated technologies and the rethinking of legacy processes and organization structures. The timing of this transformation will differ at different organizations, but the need for new thinking will be non-negotiable.

Technologies Shaping the Future of Banking
As opposed to technology taking a secondary position, supporting only the processing of transactions, future technologies will be more customer-centric and efficient, and provide more targeted, secure and intelligent solutions. With technology as the driving force in the future, organizations will be able to redefine themselves to be more competitive and responsive to marketplace needs.
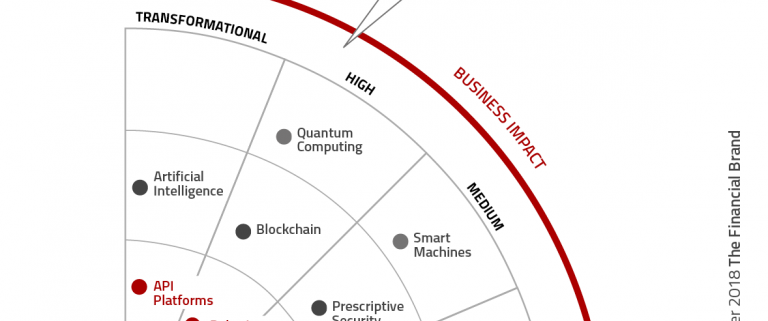
Atos developed a very helpful Global Banking Technology Radar that provides a perspective on the technologies anticipated over the next five years, the business impact of the technologies and the timing of integration. We provided a short description of each technology for better understanding.
1. Hybrid Cloud
According to IBM, cloud computing has quickly become mainstream in banking, with most banks searching for the optimal mix of traditional IT, public and private clouds. Over time, more and more banks are moving to an enterprise-wide hybrid cloud strategy.
“With hybrid cloud, banks have the flexibility and benefits of both private and public cloud, while addressing data security, governance and compliance,” states IBM. The benefits of a hybrid cloud include reduced costs, improved operational efficiency and enhanced innovation.
It was found that at least 75% of bankers said their most successful cloud initiatives had already achieved expansion into new industries, creation of new revenue streams, and expansion of their product/services portfolio.
( Read More: Platforms, Products And Channels Transforming Financial Services )
2. API Platforms
The combination of open platform banking and open APIs will change the entire banking ecosystem as we know it, from the products and services offered, to the delivery channels used and underlying partnerships that will shape innovation and customer experiences in the future. With public APIs, customers will have more options to interact with their bank.
In this scenario, the bank will serve as a platform, on top of which third-party companies can build their own applications using the bank’s data. Looking forward, the business model of retail banks, where checking accounts are used as a ‘hook’ to attract customers for more profitable lending products, may become unsustainable.
( Read More: Financial Institutions Must Explore Open Banking Options Today )

3. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Across financial services, robotic process automation (RPA) has helped banks and credit unions accelerate growth by executing pre-programmed rules across a range of structured and unstructured data. This intelligent automation gives processes the power to learn from prior decisions and data patterns to make decisions by themselves – reducing the cost of administrative and regulatory processes by at least 50% while improving quality and speed.
Robotic process automation in banking also simplifies compliance by keeping detailed logs of automated processes, automatically generating the reports an auditor needs to see, and eliminating human error. Since it’s intuitive and easy to re-configure software robots at any time, tweaking processes to fit new or updated regulations is never difficult.
( Read More: Robotics and Cognitive Automation Will Keep Banks From Drowning in Data )
4. Instant Payments
Technology has changed consumer and business expectations in payments. Instant payment options are available in many markets despite the lack of immediate payment infrastructures. In some countries, banks offering alternatives to immediate payments actively market apps to their own customers, and in some countries banks even partner together to offer an immediate P2P payment experience to a wider customer base.
The availability of an instant payments platform offers banks an enticing opportunity to achieve the transaction speed consumers expect of their banking experience and increase the customer satisfaction. With instant payments, more transactions will be made digitally instead of in cash, which means that payments will become less expensive and more user friendly. Finally, by expanding and combining instant capabilities with solutions in e- and m-commerce banks and credit unions could develop an innovative portfolio of new services.
( Read More: Banking Providers Fail to Sell Benefits of Mobile Banking and Payments )
5. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Heightened interest in AI has occurred because of both capabilities and business needs. The explosive growth of structured and unstructured data, availability of new technologies such as cloud computing and machine learning algorithms, rising pressures brought by new competition, increased regulation and heightened consumer expectations have created a ‘perfect storm’ for the expanded use of artificial intelligence in financial services.
The benefits of AI in banks and credit unions are widespread, reaching back office operations, compliance, customer experience, product delivery, risk management and marketing to name a few. Suddenly, banking organizations can work with large histories of data for every decision made.
For those firms not adopting AI, challenges such as fear of failure, siloed data sets and regulatory compliance are cited. Two of the biggest challenges that remain in banking is the absence of people experienced in data collection, analysis and application and the existence of data silos. The good news is that many data firms now have the capability to do a ‘workaround’, collecting data from across the organization.
( Read More: AI Could Destroy Traditional Banking As We Know It )

6. Blockchain
Experts say blockchain could have a transformational impact on the banking industry. Many see banks adopting blockchain technology to improve efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and security throughout the entire spectrum of financial services.
Some financial institutions have already started testing the use of blockchain for inter-bank transfers, with others testing in the space of payments, fraud reduction, know your customer, and loan processing. Many see tremendous benefits to streamlining and automating processes through smart contracts. In the end, regulators will need to create clear guidelines for banks using blockchain technology.
( Read More: What is Blockchain… And Why Should I Care? )
7. Prescriptive Security
The nature and incidence of cyber risk is unique and changing without notice, meaning that typical approaches to risk management may not be appropriate. The potential sources of cyber threats and the attack footprint are impossible to eliminate, requiring organizations to be nimble in their approach to cyber security.
More and more, advanced analytics, real-time monitoring, AI and other tools are used to detect potential threats and stop them before they strike. In the short-term, digital disruption may result in new risks and increased instability in the financial system, but in the long term, prescriptive security may improve its effectiveness.
8. Augmented and Virtual Reality
If personal user experiences can be enhanced by augmented reality (AR) or virtual reality (VR), then it can also be institutionalized by banks to revolutionize the banking industry. The possibilities are are still in early embryonic stages, with testing being done worldwide.
 For instance, the Commonwealth Bank of Australia targets bank customers looking to buy or sell a home. Augmented reality and rich data are used to provide historical information about property sales, price tendencies, current listings, and properties that have been sold in the area. This insight helps individuals make smart sale and purchase decisions.
For instance, the Commonwealth Bank of Australia targets bank customers looking to buy or sell a home. Augmented reality and rich data are used to provide historical information about property sales, price tendencies, current listings, and properties that have been sold in the area. This insight helps individuals make smart sale and purchase decisions.
According to analysts, augmented reality and virtual reality could be utilized to give bank customers autonomy in terms of at-home banking. Hybrid bank branches could also come into existence.
( Read More: Will Augmented and Virtual Reality Replace the Bank Branch? )
9. Quantum Computing
According to FedTech, quantum computing harnesses the laws of quantum mechanics to carry out complex data operations. While traditional computers use bits (represented as either binary 1s or 0s), quantum computing harnesses quantum bits, known as qubits. These can be read as 1s, 0s, or both, providing exponential computing power over traditional computers by creating shortcuts in the computing process.
Quantum computing represents a major leap forward in computing power, surpassing the potential of the cloud or blockchain. However, it will likely be years before it is widely used in business applications, due to many stability and security concerns. Despite this extended timeline, firms like JPMorgan and Barclays are part of a group investigating quantum computing potential in conjunction with IBM.

10. Smart Machines
The impact of smart machines (smart vision systems, virtual customer assistants, virtual personal assistants, smart advisors, other natural-language processing technologies, etc.) will have on financial institutions during the next few years is beginning to take shape.
From applications for Amazon’s Alexa to bank developed virtual assistants like Bank of America’s Erica, the future of smart machines acting as digital concierges on behalf of consumers is upon us. The banks and credit unions that invest in better digital engagement will have more profitable relationships with customers. At the end of the day, customers will continue to self-select the bank that provides the least amount of friction and the most relevant support and guidance.
( Read More: Secret To Digital Banking Success is AI With ‘Human-Like’ Feel )
Can the Banking Industry Keep Pace With Emerging Technologies?
 As quickly as past technologies have become the norm, a new wave of emerging technologies will combine digital technologies and the power of data to set new standards. The prioritization and investment in each of these technologies will vary based on the business model and strategic goals of each organization. For instance, while the marketplace as a whole does not foresee investing much in blockchain technology, the financial services industry ranks this as a high priority.
As quickly as past technologies have become the norm, a new wave of emerging technologies will combine digital technologies and the power of data to set new standards. The prioritization and investment in each of these technologies will vary based on the business model and strategic goals of each organization. For instance, while the marketplace as a whole does not foresee investing much in blockchain technology, the financial services industry ranks this as a high priority.
Most organizations recognize that there is a significant skills gap that puts transformation efforts at risk. According to PwC, “Respondents say skills in their organization lag across a range of highly important areas, including cybersecurity and privacy, business development of new technologies and user experience and human-centered design. Worse, skill levels have declined even as the demands of digital keep advancing.”
It is important for all financial organizations to make emerging technology a ‘core competency,’ with engagement throughout the organization (not just the very top). In addition, the focus of every implementation must be both internal and external human experiences, as opposed to revenue, profit and cost savings.